gold foil experiment results|Size of the Nucleus : Clark The Geiger–Marsden experiments (also called the Rutherford gold foil experiment) were a landmark series of experiments by which scientists learned that every atom has a nucleus where all of its positive charge and most of its mass is concentrated. They deduced this after measuring how an alpha particle beam is scattered when it strikes a thin metal foil. The experiments were performed b. Exclusive hot m2m pinoy videos, solo jakol, group fun, alter fun, scandal and more. PINOY JAKOL BOYS 🇵🇭🏳️🌈 . Perkhidmatan tidak rasmi untuk Rasul Telegram .
PH0 · What is the 'Gold Foil Experiment'? The Geiger
PH1 · Size of the Nucleus
PH2 · Rutherford’s gold foil experiment (video)
PH3 · Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment
PH4 · Rutherford model
PH5 · Models of the atom
PH6 · Geiger–Marsden experiments
PH7 · Ernest Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment
PH8 · Discovery of the electron and nucleus (article)
PH9 · About Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment
PH10 · 4.14: Gold Foil Experiment
PH11 · 3.4: Rutherford's Experiment
Lava and smoke or a geyser of fire spews from one or both of the volcanoes on Camerupt's back, also making flaming rocks fly in all directions. Vicky Winstrate's Camerupt: Candid Camerupt! Debut: A Coordinator's Camerupt: A Cacturne for the Worse: None: A student's rental Camerupt: One Team, Two Team, Red Team, Blue .
gold foil experiment results*******In 1911, Rutherford and coworkers Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden initiated a series of groundbreaking experiments that would completely change the accepted model of the atom. They bombarded very thin sheets of gold foil with fast moving alpha particles. Alpha particles, a type of natural radioactive . Tingnan ang higit paThis action is not available. How much space do bricks occupy? As we look at the world around us, it looks pretty solid. We hit a wall with our hand and the hand stops – it does not (normally) go through the wall. We . Tingnan ang higit paBombardment of gold foil with alpha particles showed that a very small percentage of alpha particles were deflected. The nuclear model of the atom consists of a small and dense positively charged . Tingnan ang higit paThe Geiger–Marsden experiments (also called the Rutherford gold foil experiment) were a landmark series of experiments by which scientists learned that every atom has a nucleus where all of its positive charge and most of its mass is concentrated. They deduced this after measuring how an alpha particle beam is scattered when it strikes a thin metal foil. The experiments were performed b. Features. The gold foil experiment consisted of a series of tests in which a positively charged helium particle was shot at a very thin layer of gold foil. The expected result was that the positive particles .
Gold was used because it was the only metal that could be rolled out to be very, very thin without cracking. It was thought that the alpha particles could pass straight through the . The Geiger-Marsden experiment, also called the gold foil experiment or the α-particle scattering experiments, refers to a series of early-20th-century .Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space with a tiny, dense, positively-charged nucleus. Based on these results, Rutherford proposed the .
The gold-foil experiment showed that the atom consists of a small, massive, positively charged nucleus with the negatively charged electrons being at a great distance from the centre. Niels Bohr built upon .
Alpha particles only have 2 protons, so the positive charge is not strong enough to attract the electrons in the gold atom. It might have definitely interacted, with the electrons . Rutherford demonstrated his experiment on bombarding thin gold foil with alpha particles contributed immensely to the atomic theory by proposing his nuclear atomic model. The nuclear model of the atom . Describe Rutherford's gold foil experiment and explain how this experiment altered the "plum pudding" model. The electron was discovered by J.J. .
Rutherford directed beams of alpha particles at thin gold foil to test this model and noted how the alpha particles scattered from the foil. In the experiment, Rutherford showed us that the atom was mainly empty .A few even bounced backward. The only way this would happen was if the atom had a small, heavy region of positive charge inside it. What is the Rutherford gold-foil experiment? A piece of gold foil was hit with alpha particles, which have a positive charge. Most alpha particles wen. The Gold Foil Experiment. In 1911, Rutherford and coworkers Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden initiated a series of groundbreaking experiments that would completely change the accepted model of the atom. They bombarded very thin sheets of gold foil with fast moving alpha particles.gold foil experiment results Size of the Nucleus The gold foil experiment results in the Rutherford model, where the atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. In 1911, Rutherford and coworkers Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden initiated a series of groundbreaking experiments that would completely change the accepted model of the atom. They bombarded very thin sheets of gold foil with fast moving alpha particles. Figure 3.4.2 3.4. 2 (a) The experimental setup for Rutherford's gold foil experiment: A .
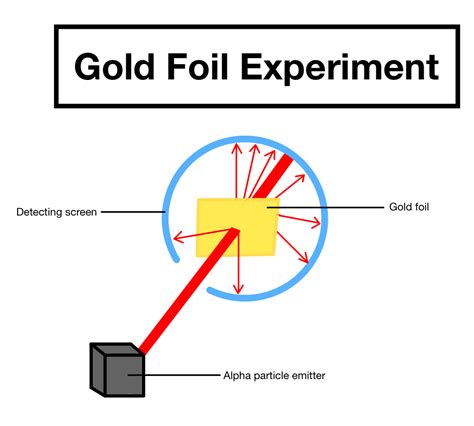
Well, the electrons of the gold atom were held there by the nucleus (or the 79 protons) of the gold atom.Alpha particles only have 2 protons, so the positive charge is not strong enough to attract the electrons in the gold atom.It might have definitely interacted, with the electrons "pulling" them toward themselves, which result in a tiny force which pushed the . The gold foil experiment was a pathbreaking work conducted by scientists Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden under the supervision of Nobel laureate physicist Ernest . a vastly empty atom holds a tiny nucleus at the center surrounded by a cloud of electrons. As a result of his gold foil experiment, Rutherford’s atomic theory holds good even .The Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment offered the first experimental evidence that led to the discovery of the nucleus of the atom as a small, dense, and positively charged atomic core. . Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden discovered that atoms indeed scattered alpha particles, a experimental result completely contrary to Thompson's model of the .gold foil experiment resultsThe Rutherford atomic model relied on classical physics. The Bohr atomic model, relying on quantum mechanics, built upon the Rutherford model to explain the orbits of electrons. What were the results of Rutherford's experiment? The previous model of the atom, the Thomson atomic model, or the “plum pudding” model, in which neg.Size of the Nucleus The experiments were performed between 1908 and 1913 by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden under the direction of Ernest Rutherford at the Physical Laboratories of the University of Manchester. In the experiment, Rutherford sent a beam of alpha particles (helium nuclei) emitted from a radioactive source against a thin gold foil (the thickness of .Rutherford conducted an experiment by bombarding a thin sheet of gold with α-particles and then studied the trajectory of these particles after their interaction with the gold foil. Rutherford, in his experiment, directed .
The gold-foil experiment disproved J.J. Thomsons plum pudding model, which hypothesized the atom was positively charged spaced with electrons embedded inside. Therefore, giving way to the nuclear model. In this .In 1905, Ernest Rutherford did an experiment to test the plum pudding model. His two students, Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, directed a beam of alpha particles close alpha particle Subatomic .

ANSWER: A. The Rutherford scattering experiment directed parallel beams of α-particles at gold foil. The observations were: Most of the α-particles went straight through the foil. The largest value of n will therefore be at small angles. Some of the α-particles were deflected through small angles. n drops quickly with increasing angle of .
The experimental results of either case above will be very much the same. There would be small differences, however, which may be able to determine which case is actually correct. In the . Modification of the gold foil experiment may also help to determine which case is valid. If the alpha particles were to be show slowly in the gold foil .The Rutherford model of the atom is a model of the atom devised by the British physicist Ernest Rutherford. Rutherford’s new model for the atom is based on the experimental results obtained from the Geiger-Marsden experiments (also called the Rutherford gold foil experiment).The Geiger–Marsden experiments were performed between 1908 and .
Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment (Geiger-Marsden Experiment). Rutherford teamed up with his assistant, Hans Geiger and Ernst Marsden who was an undergraduate student working in Rutherford’s lab; conducted “Gold Foil Experiment” also known as the Geiger-Marsden experiment.His idea was to probe the structure of Atom by firing α-particles or .
Rutherford's diffraction experiment tests diffraction via a thin foil made of gold metal. Opposite the gold foil is a screen that emits a flash of light when struck by a particle. The passing of many of the particles through suggested the condensed nucleus version of the atom model.
Welcome to the William Hill Vegas Casino app! Experience real money slots, gambling and go Beyond Entertainment with a wide range of online casino slots, live casino games, online Roulette, Blackjack, Poker and Bingo. Plus, look out for a variety of weekly casino, roulette, or blackjack promotions. There could be free spins, bonuses or cash .
gold foil experiment results|Size of the Nucleus